In this tutorial we are going to see about GenericServlet with example program.
A Servlet is just normal class which implements the Interface Servlet
The following classes implements the Servlet Interface.
GenericServlet defines a generic, protocol-independent Servlet.We can create protocol independent Servlet by extends GenericServlet .To write an HTTP Servlet for use on the Web, extend HttpServlet instead.
GenericServlet implements the Servlet and ServletConfig interfaces. GenericServlet may be directly extended by a Servlet , although it's more common to extend a protocol-specific subclass such as HttpServlet.
GenericServlet makes writing Servlet easier. It provides simple versions of the lifecycle methods init and destroy and of the methods in the ServletConfig interface. GenericServlet also implements the log method, declared in the ServletContext interface.
To write a generic servlet , you need only override the abstract service method.
Now see how to create GenericServlet with example.
1. Create new Dynamic web project by choosing File –> New –> Dynamic Web Project .
2. Create the Project called ServletExample as given below.

3. Create package called com.javatutorialscorner.servlet under ServletExample.
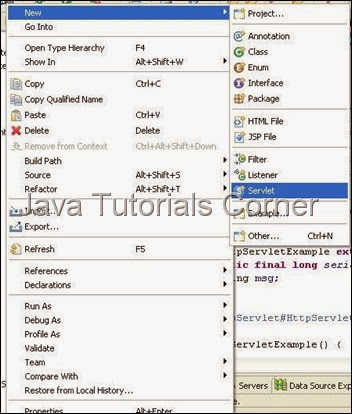
4. Create Servlet called GenericServletExample as shown in figure. (By default super class in eclipse servlet creation is HttpServlet, change it into javax.servlet.GenericServlet)

5. Click Next it will show URL mapping.You can edit Servlet URL if you need.
6. Click Next it will show methods available in GenericServlet. Select appropriate method you need. service() method is mandatory one.

7. By default your servlet will be mapped in web.xml, if your servlet not mapped in your web.xml use the following configuration to map the servlet in your web.xml
Servlet Mapping
web.xml
8. Add the required code inside service() method.
GenericServletExample.Java
9. Now save and Run the servlet , Run As –> Run on Server – Select your web Server to run the servlet. ( see How to configure tomcat in eclipse)
10.call the URL which is mapped in web.xml.
Output

A Servlet is just normal class which implements the Interface Servlet
javax.servlet.Servlet
The following classes implements the Servlet Interface.
import javax.servlet.GenericServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
GenericServlet defines a generic, protocol-independent Servlet.We can create protocol independent Servlet by extends GenericServlet .To write an HTTP Servlet for use on the Web, extend HttpServlet instead.
GenericServlet implements the Servlet and ServletConfig interfaces. GenericServlet may be directly extended by a Servlet , although it's more common to extend a protocol-specific subclass such as HttpServlet.
GenericServlet makes writing Servlet easier. It provides simple versions of the lifecycle methods init and destroy and of the methods in the ServletConfig interface. GenericServlet also implements the log method, declared in the ServletContext interface.
To write a generic servlet , you need only override the abstract service method.
Now see how to create GenericServlet with example.
1. Create new Dynamic web project by choosing File –> New –> Dynamic Web Project .
2. Create the Project called ServletExample as given below.

3. Create package called com.javatutorialscorner.servlet under ServletExample.
4. Create Servlet called GenericServletExample as shown in figure. (By default super class in eclipse servlet creation is HttpServlet, change it into javax.servlet.GenericServlet)


5. Click Next it will show URL mapping.You can edit Servlet URL if you need.
6. Click Next it will show methods available in GenericServlet. Select appropriate method you need. service() method is mandatory one.

7. By default your servlet will be mapped in web.xml, if your servlet not mapped in your web.xml use the following configuration to map the servlet in your web.xml
Servlet Mapping
<servlet>
<servlet-name>Your Servlet Name</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>Fully Qulaified Servlet Class Name</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Your Servlet Name</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/URL to Call Servlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0">
<display-name>ServetExample</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>GenericServletExample</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.javatutorialscorner.servlet.GenericServletExample</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>GenericServletExample</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/GenericServletExample</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
8. Add the required code inside service() method.
GenericServletExample.Java
package com.javatutorialscorner.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.GenericServlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
/**
* Servlet implementation class GenericServletExample
*/
public class GenericServletExample extends GenericServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String msg;
/**
* @see GenericServlet#GenericServlet()
*/
public GenericServletExample() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
/**
* @see Servlet#init(ServletConfig)
*/
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
msg = "Java Tutorials Corner Hello World Servlet Program";
}
/**
* @see Servlet#destroy()
*/
public void destroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
/**
* @see Servlet#getServletConfig()
*/
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
/**
* @see Servlet#getServletInfo()
*/
public String getServletInfo() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
/**
* @see Servlet#service(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
*/
public void service(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.write("<html><body><h2>" + msg + "</h2></body></html>");
}
}
9. Now save and Run the servlet , Run As –> Run on Server – Select your web Server to run the servlet. ( see How to configure tomcat in eclipse)
10.call the URL which is mapped in web.xml.
Output






0 comments:
Post a Comment